|
 |
|||||||
| July 14, 2011 | Research Extras Construction of a new Health Sciences Research Building on the Emory campus began with an official groundbreaking June 15. More than half of the new facility on Haygood Drive will focus on pediatric research through the Emory-Children's Pediatric Research Center, a partnership between Emory and Children's Healthcare of Atlanta. iResearch Georgia is a searchable database of biomedical expertise at Georgia's public and private research universities. Users can view profiles, published papers, and NIH grant abstracts of more than 800 scientific leaders across the state. The database is meant to enhance collaboration among universities and help industry identify experts and projects with commercial potential. It is an initiative of the Georgia Research Alliance in partnership with the University System of Georgia, the Governor's Commission for a New Georgia and the Georgia Department of Economic Development.
|
|||||||
|
Randy Trumbower with a glove that measures the effects of hypoxia on hand function |
||||||||
Sound Science: Can Less Oxygen = More Movement in Spinal Cord Injuries? |
||||||||
|
Chris Larsen and Tom Pearson
|
||||||||
| FDA Approves Transplant Drug That Preserves Kidneys, Avoids Toxicity Emory transplant surgeon/scientists have led a two-decades effort to develop better drugs to prevent transplant rejection. The FDA has approved Nulojix (belatacept) as a potentially less toxic alternative to the drugs used by most kidney transplant patients. It also is being tested in clinical trials of liver and islet transplants. Read more... |
||||||||
| Microneedle Vaccine Protects Better Against H1N1 Flu Than Injection Mice immunized against H1N1 flu with a skin patch of coated microneedles were still immune six months later, while mice immunized subcutaneously had a 60 percent decrease in antibody production as well as lung inflammation. Emory and Georgia Tech scientists have developed dissolving microneedle vaccine patches that could be easy and effective for flu protection. Read more... |
||||||||
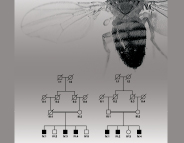
| Mutant Flies Shed Light on Inherited Intellectual Disability Clumsy fruit files with poor posture are helping scientists understand inherited intellectual disability in humans, and vice versa. The flies can't hold their wings tightly against their bodies, and have trouble flying and climbing, because they have mutations in a gene called dNab2. In humans, mutations in the same gene (called ZC3H14) have been found to cause intellectual disability. Read more... |
||||||||
|
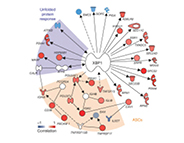
Scientists use systems biology to search for genes involved in antibody production
|
||||||||
| Quick Test Can Predict Immune Response to Flu Shots Thus far it's been hard to know in advance who will benefit from a flu vaccine. Scientists have developed a new test to predict within days of vaccination whether a person will produce high levels of flu antibodies four weeks later. This could help in developing better vaccines and in monitoring immune responses in vulnerable groups, such as the elderly, infants, or those with weakened immune systems. Read more... |
||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||