 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
   |

 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
 |
June 8, 2012 |
 |
Find out more about Saint Joseph's Translational Research Institute (SJTRI) and opportunities for research collaboration.
Read vaccine researcher Mark Mulligan's commentary from HIV Vaccine Awareness Day: Why We Still Need an HIV Vaccine.
Worldwide, more than 325,000 babies are born annually with neural tube birth defects – and 75 percent of these defects could have been prevented with folic acid. The Rollins School of Public Health and the Department of Pediatrics, in partnership with Sophie's Voice Foundation, are launching a Spina Bifida Research and Prevention Center to fight this disease.
Read the Spring issue of Emory Nursing magazine for stories about global health and research, notable faculty projects and life-changing field work in the U.S.
|
 |
| |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
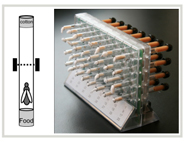
 Tubes with infrared sensors track flies' sleep behavior
Tubes with infrared sensors track flies' sleep behavior |
| |
|
|
|
|
Sleepless Flies Point to Genetic Link for Restless Legs Syndrome
A gene linked to human restless legs syndrome (RLS) has been found to disturb sleep in fruit flies. Mutations in the gene BTBD9 cause flies to wake up more often during sleep periods, which is a key symptom of human RLS. The same mutation also reduces levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the flies, and dopamine deficiency is thought to be behind RLS in humans also. Read more... |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
The Emory Cancer Genomics Center Team
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Cancer Genomics Center Targets Protein Networks for Drug Discovery
The National Cancer Institute has chosen Emory as the site of a new center focusing on cancer genome and drug discovery research. Alterations in genes are known to be involved in many cancer types, but the new center will sift out interactions between proteins that are "rewired" in tumor development. Researchers plan to develop drugs that will interfere with these protein networks and halt tumor progression. Read more... |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
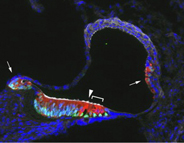

Regenerating mature sensory hair cells (red) in the cochlea |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Gene Therapy Research Shows Potential as Hearing Loss Treatment
Sensory hair cells produce electrical signals in response to vibrations in the inner ear and connect with neurons to allow hearing to occur. Regenerating these cells, which diminish in some cases of age- and trauma-related hearing loss, could help treat the condition. Researchers have shown that a gene called Atoh1 can stimulate the formation of extrasensory hair cells in the cochleae of young mice. Read more... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |

Peng Jin, PhD

|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Restricting Iron in Cells Could Help Shut Down Genes as Therapy for Challenging Diseases
Drugs that bind dissolved iron (iron chelators) have been tested as a possible treatment for cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative diseases, because these diseases may thrive with extra iron. Researchers have found that iron chelators regulate RNA interference, a method of selectively shutting off genes. The discovery could help them focus on RNA in diseases where iron plays a role. Read more... |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |

A new breath analyzer could help diagnose lung cancer
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Breath Test Shows Promise for Early Diagnosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Emory and Georgia Tech researchers found 75 unique breath compounds in a small study of patients with non-small cell lung cancer vs. people without the disease. While promising, the results require testing in larger studies before routine use. If proven, a simple and inexpensive test for early detection could have a big impact on diagnosing this challenging cancer. Read more... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |








